Your power supply unit (PSU) is the heart of your computer system, providing the necessary energy to keep all components running smoothly. However, like any other hardware component, power supplies can degrade over time, potentially leading to system instability, crashes, or complete failure.
Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to maximize the lifespan of your PSU and ensure your system remains reliable for years to come.
Buy a High-Quality Model
Investing in a high-quality power supply from the outset is one of the most effective ways to ensure longevity. Look for models with an 80 Plus certification, which indicates high energy efficiency and lower heat output. Consider researching professional reviews for specific models to gauge their reliability and performance.
Purchasing a quality PSU designed with strong components and rigorous testing reduces the chances of premature failure or unexpected burnout. While a high-quality unit may come at a higher upfront cost, it can save you money in the long run with a longer lifespan and better efficiency.
Give Your PSU Proper Ventilation

Adequate ventilation is crucial for maintaining optimal operating temperatures and prolonging the lifespan of your power supply. Here are some tips to ensure proper ventilation:
- Provide ample clearance around the PSU: When installing your power supply, ensure there is sufficient space around it for air to circulate freely. Avoid cramming it into tight spaces or obstructing the air intake and exhaust vents.
- Use cable management: Tangled cables can restrict airflow and trap heat, increasing temperatures inside your case. Invest in cable management solutions to keep cables organized and tidy, allowing for better airflow.
- Consider case fans: Strategically placed case fans can help maintain a consistent cool-air flow over your energy supply, dissipating heat more effectively.
- Monitor temperatures: Use monitoring software or hardware sensors to watch your PSU’s operating temperatures. If temperatures consistently exceed recommended levels, promptly investigate and address any ventilation issues.
Keep Your Power Supply Clean and Dust-Free
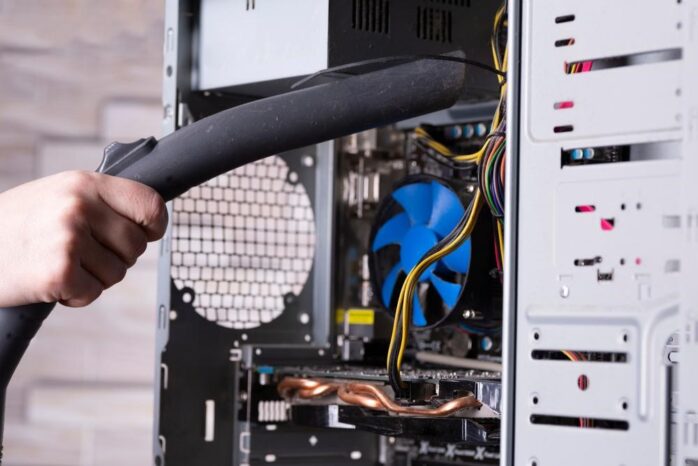

Over time, dust and debris can accumulate inside your power supply, clogging air vents and impeding airflow. This buildup can lead to increased operating temperatures, reduced efficiency, and a potentially shorter lifespan.
Aim to clean your PSU at least every three months to prevent these issues. Consider a more frequent cleaning schedule if your environment is dusty.
Follow these steps:
- Turn off and unplug your PC: Safety first! Always ensure your system is completely off before opening the case.
- Open the case: Following your case manufacturer’s instructions, carefully open your PC case and access the PSU.
- Use compressed air: Use a can of compressed air to gently blow dust out of the PSU’s vents and internal components. Hold the can upright to avoid condensation and avoid spraying directly on delicate components to prevent damage.
- Vacuum (optional): You can use a vacuum cleaner with a soft brush attachment to remove stubborn dust bunnies for a more thorough cleaning. Be very gentle and avoid touching any components with the nozzle to avoid damaging them.
- Reassemble: Once you’re finished cleaning, carefully reassemble your PC case and reconnect all cables.
Invest in a Surge Protector
Power surges and voltage spikes can wreak havoc on your supply and other sensitive components. These sudden increases in electrical current can cause rapid wear and tear, potentially leading to premature failure or, in extreme cases, even overheating or fire.
Invest in a high-quality surge protector to protect your power supply (and your entire system) from these damaging events. Surge protectors act as a buffer, absorbing and diverting excess voltage away from your devices, preventing damage.
When choosing a surge protector, look for models with high joule ratings (a measure of their energy absorption capacity) and fast response times. Consider models with built-in circuit breakers or automatic shutoff features for added protection against prolonged power surges.
If you suspect a problem with your power supply, testing it can help you determine if it needs a replacement. Here’s how to test a power supply:
- Disconnect all components from the power supply, leaving only the 24-pin and CPU power connectors attached.
- Use a power supply tester or a multimeter to check the voltage outputs.
- Short the green wire (power on) to any black ground wire to start the energy supply.
- Check if the fan spins and the voltages are within acceptable ranges (typically +/- 5 percent of the rated voltage).
- If the voltages are incorrect or the fan doesn’t spin, the power supply may be faulty and require replacement.
Regular testing can help identify potential issues before they cause system failures, allowing you to proactively replace the power supply and prevent data loss or damage to other components.
Avoid Overloading Your Supply

The watt rating of your power supply unit is a crucial factor in ensuring the longevity and reliability of your system. This rating indicates the maximum power the PSU can deliver to your computer’s components. Exceeding this limit by overloading the PSU can lead to premature wear and tear, potentially causing it to fail or risk damaging other components.
It’s essential to calculate your machine’s total power consumption accurately. All PC components consume power at varying rates, depending on their specifications and usage patterns. For instance, an idle gaming PC consumes less power than one running a demanding game, as the CPU and GPU are not used to their full potential during idle periods.
However, your system’s power consumption will increase when you run resource-intensive applications or games. Components like the CPU and GPU operate at higher loads. This increased power draw might overload an underpowered PSU, causing it to overload and generate more heat, leading to accelerated wear and potentially catastrophic failure.
Accurately estimating your system’s total power consumption is crucial to avoid overloading your PSU. PC builders often incorporate tools like an estimated wattage calculator to assist with this.
These calculators consider the specifications of your components, such as the CPU, GPU, storage devices, and other peripherals, to provide an estimated requirement for your build.
Maximize Your PSU’s Lifespan
By following these practices, you can effectively extend your PSU’s lifespan and ensure it delivers reliable power for years. Remember — a healthy PSU is the backbone of a stable and reliable PC system, and with some preventive care, you can keep it operating for many years.